Key Takeaways
- Mulches vegetation on-site, enriching soil and reducing erosion.
- Safer and more sustainable than burning or hauling debris.
- Key uses: wildfire prevention, invasive species control, and land prep.
- Supports ecosystems while improving property value.
- A growing solution for sustainable land management.
Introduction: The Basics of Forestry Mulching
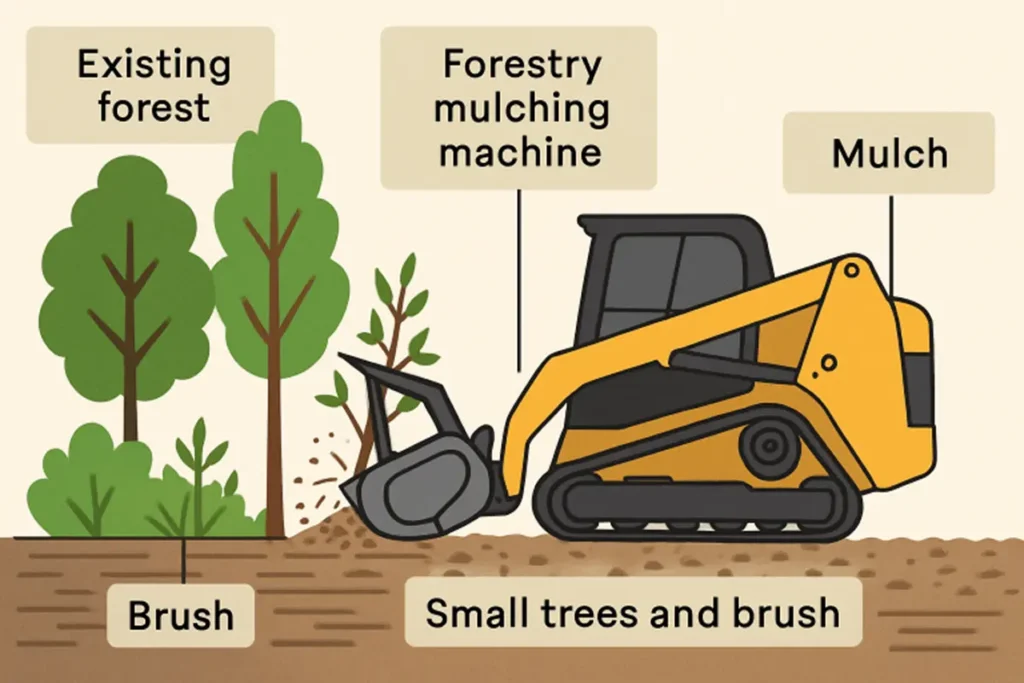
Forestry mulching is an advanced land management technique in which specialized machinery clears, cuts, and grinds vegetation such as trees, shrubs, and brush right where it stands. Instead of hauling away debris, the process converts organic matter into a nutrient-rich mulch layer left on the forest floor. This method benefits property owners, environmental stewards, and anyone managing large tracts of overgrown or forested land.
Forestry mulching’s primary uses include wildfire risk reduction, ecosystem restoration, and the promotion of healthier woodlands. Increasingly, landowners are turning to forestry mulching in Front Royal for effective, sustainable vegetation management and land improvement strategies. By mechanically shredding and dispersing unwanted undergrowth, forestry mulching not only opens up landscapes but also preserves valuable topsoil.
How Does Forestry Mulching Work?
The central component of forestry mulching is the machine usually a skid steer, tracked loader, or tractor equipped with a rotary drum or disc mulcher. These robust machines can take down trees and thick brush and grind the material into a layer of mulch as they move through the landscape. Attachments vary based on the job size and vegetation type, but all are designed to shred debris on the spot.
The process begins with an assessment and plan. Operators identify which vegetation should be removed, which areas require preservation, and any unique site constraints. Once on-site, machines are maneuvered safely and efficiently to mulch unwanted growth, leaving behind a uniform layer of organic material. The result is a cleared and mulched area with minimal soil disturbance.
Unlike traditional land clearing, where vegetation is pulled, uprooted, or burned, forestry mulching quietly and swiftly reduces biomass, avoiding soil compaction issues or removing native seed banks.
Step-by-Step Forestry Mulching Process
Assessment of Land and Planning
Every effective forestry mulching project begins with a careful evaluation of the landscape. Professionals inspect the property, noting topography, sensitive habitats, and desired outcomes. This step removes only targeted vegetation, preserving beneficial plants and minimizing environmental impact.
Equipment Set-Up and Safety Measures
Before machinery enters the field, all equipment undergoes stringent safety checks. Operators wear personal protective equipment (PPE), including helmets, gloves, eye protection, and steel-toed boots. Safety zones are established to keep bystanders at a safe distance, and crews review emergency protocols before starting work.
Mulching in Action: Breaking Down Vegetation
With plans in place and safety precautions observed, the mulching process begins. Machines enter the area and systematically grind selected vegetation. The mulcher head spins rapidly, shredding trees, saplings, and brush into fine mulch. This action continues until all targeted growth is thoroughly processed. Operators monitor for any obstacles, adjusting machinery as needed to protect desirable plants or infrastructure.
Site Clean-Up and Post-Mulching Inspection
After mulching, the site is inspected to confirm that all work aligns with the original plan. Operatives may redistribute mulch for even coverage, remove any remaining large debris, and document the project’s success. This final review ensures a safe, visually appealing, and ecologically sound outcome.
Environmental Benefits of Forestry Mulching
One of the strongest arguments for forestry mulching is its positive environmental impact. By leaving a layer of shredded organic matter, the process reduces soil erosion and helps retain moisture. This improves soil structure and fertility, especially on sloped or sensitive lands.
The natural mulch layer also benefits local ecosystems—offering cover and nesting material for small wildlife, retaining seeds, and preserving beneficial microorganisms. Unlike burning or hauling debris, forestry mulching recycles nutrients directly into the ground, enriching the site long-term.
Common Uses for Forestry Mulching
- Firebreak Creation: Dense forests and overgrown brush can be hazardous in fire-prone regions. By clearing strategic corridors, forestry mulching creates firebreaks that slow or halt the spread of wildfires, offering protection to nearby properties and habitats.
- Invasive Species Control: Rapidly spreading invasive plants can choke out native ecosystems. Forestry mulching targets and destroys these species, promoting healthier landscapes and encouraging the return of native flora.
- Land Clearing for Agricultural and Recreational Purposes: Whether preparing fields for crops, opening trails, or reclaiming pastures, mulching offers a fast, efficient, and environmentally responsible solution for landowners.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Safety is paramount in any forestry mulching operation. Operators must wear PPE such as hard hats, hearing protection, and high-visibility clothing. Equipment checks are mandatory before and during work to ensure that all mechanical systems function properly.
It’s also essential to check local regulations, ensure all operators are trained and licensed for specialized machinery, and use best practices to minimize risks to people, wildlife, and property.
Sustainable Land Management and the Future of Forestry Mulching
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, forestry mulching is set to play a key role in future land management. Its effectiveness in reducing wildfire risk, restoring habitats, and supporting carbon sequestration has been widely recognized. Innovations in mulching equipment and techniques make it faster, quieter, and more eco-friendly.
According to research from the U.S. Forest Service, emerging trends include precision mulching, improved machine efficiency, and integration with broader landscape restoration efforts. As more landowners and conservationists embrace these methods, forestry mulching continues to set a benchmark for low-impact, high-value land stewardship.
Final Thoughts
Forestry mulching offers a modern, eco-conscious solution for managing overgrown or wooded properties. Combining efficiency with environmental responsibility provides landowners and conservationists with a method that enhances landscapes while preserving soil health and biodiversity. With its versatility from wildfire mitigation to habitat restoration forestry mulching is more than a clearing technique; it is a long-term investment in healthier, more resilient land.